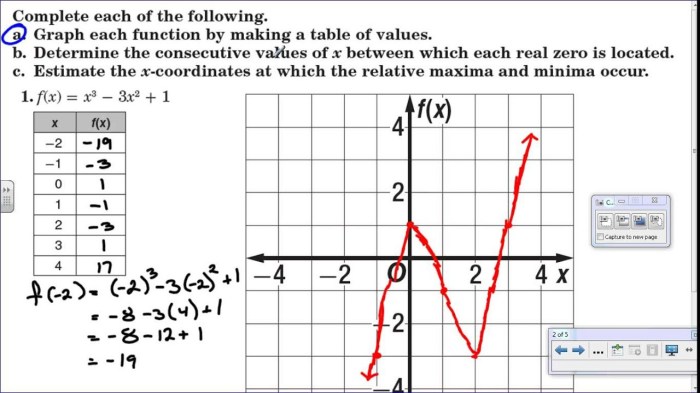
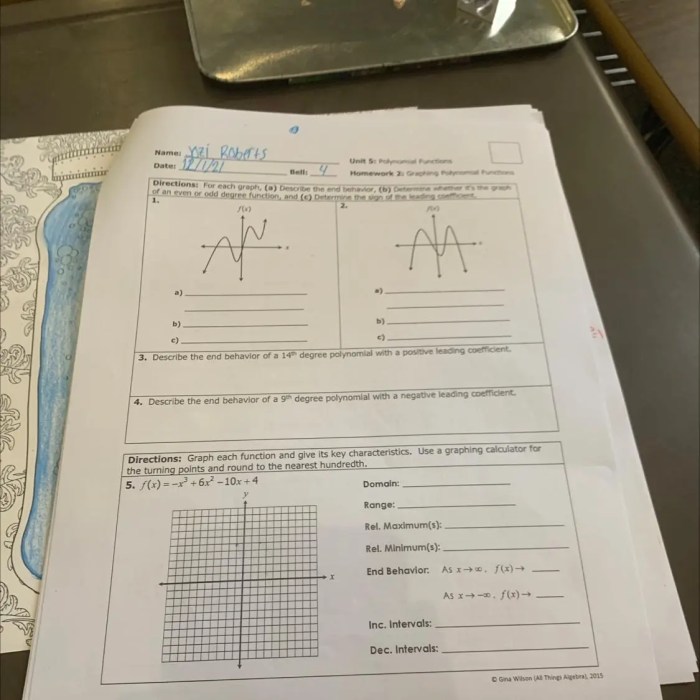
Delve into the captivating world of homework 2 graphing polynomial functions, where intricate curves and equations unravel secrets that shape our understanding of the world around us. This comprehensive guide embarks on a journey to unveil the fundamental principles, techniques, and applications of polynomial functions, empowering you to conquer the challenges of graphing with precision and confidence.
As we navigate the intricacies of polynomial functions, we will explore their diverse forms, uncover the relationship between their degree and their graphical representation, and delve into the practical applications that make them indispensable tools in various fields.
1. Graphing Polynomial Functions: Homework 2 Graphing Polynomial Functions
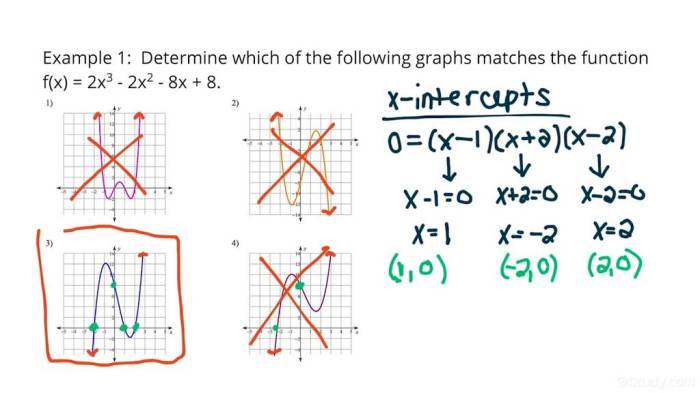
Polynomial functions are a type of function that can be represented by a polynomial expression. The graph of a polynomial function is a curve that can be used to visualize the relationship between the input and output values of the function.
The basic principles of graphing polynomial functions involve understanding the shape of the curve and how it is affected by the degree and coefficients of the polynomial.
There are different types of polynomial functions, each with its own characteristic graph. The degree of a polynomial function is the highest exponent of the variable in the polynomial expression. The degree of the polynomial determines the number of turning points (local maxima and minima) in the graph.
2. Techniques for Graphing Polynomial Functions
There are several techniques that can be used to graph polynomial functions, including:
- Factoring:Factoring the polynomial expression can help identify the x-intercepts and the shape of the graph.
- Synthetic division:Synthetic division can be used to find the roots of the polynomial and the corresponding y-intercepts.
- The Rational Root Theorem:The Rational Root Theorem can be used to find possible rational roots of the polynomial, which can help identify the x-intercepts.
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific polynomial function and the desired level of accuracy.
3. Applications of Graphing Polynomial Functions
Graphing polynomial functions has applications in various fields, including:
- Physics:Polynomial functions can be used to model the trajectory of projectiles, the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, and the behavior of springs.
- Engineering:Polynomial functions can be used to design bridges, buildings, and other structures, and to analyze the performance of mechanical systems.
- Economics:Polynomial functions can be used to model supply and demand curves, production functions, and consumer behavior.
Understanding how to graph polynomial functions is essential for solving problems in these fields and making informed decisions.
4. Common Pitfalls in Graphing Polynomial Functions
Common mistakes students make when graphing polynomial functions include:
- Incorrectly identifying the x- and y-intercepts:It is important to use the correct techniques to find the intercepts.
- Not considering the end behavior:The end behavior of the graph should be determined by examining the highest degree term of the polynomial.
- Making errors in calculations:Care should be taken to avoid errors when factoring, using synthetic division, or applying the Rational Root Theorem.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires careful attention to detail and a solid understanding of the principles of graphing polynomial functions.
5. Advanced Topics in Graphing Polynomial Functions, Homework 2 graphing polynomial functions
Advanced concepts related to graphing polynomial functions include:
- Asymptotes:Vertical and horizontal asymptotes can be used to determine the limits of the graph.
- Concavity:The concavity of the graph can be determined by examining the second derivative of the polynomial.
- End behavior:The end behavior of the graph can be determined by examining the highest degree term of the polynomial.
These concepts provide a deeper understanding of the behavior of polynomial functions and can be used to analyze and interpret their graphs.
General Inquiries
What is the relationship between the degree of a polynomial function and its graph?
The degree of a polynomial function determines the number of turning points in its graph. A polynomial function of degree n will have at most n-1 turning points.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of factoring, synthetic division, and the Rational Root Theorem for graphing polynomial functions?
Factoring is useful for graphing polynomial functions that can be easily factored. Synthetic division is a quick and efficient method for finding the roots of a polynomial function. The Rational Root Theorem can be used to find rational roots of a polynomial function.
What are some common mistakes students make when graphing polynomial functions?
Common mistakes include not finding all the roots of the polynomial function, not plotting the points correctly, and not drawing the graph accurately.