Which risk is common with both tanning and tattoos? This question delves into the realm of skin health, exploring the potential hazards associated with these popular practices. From the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation to the potential for infections and allergic reactions, we uncover the hidden risks that lie beneath the golden glow of a tan and the vibrant hues of a tattoo.
Tanning and tattooing, while seemingly distinct, share a common thread: the potential for skin damage. Understanding the risks associated with both practices empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their skin health.
Skin Damage
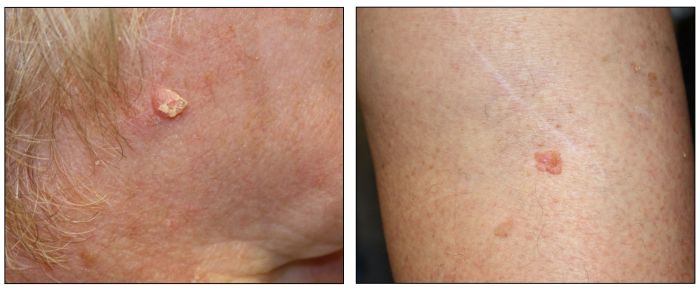
Tanning and tattooing both involve exposing the skin to harmful agents that can cause damage. UV radiation from tanning beds or the sun can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer. Tattoo ink, which is composed of pigments and other chemicals, can also cause skin damage, including inflammation, allergic reactions, and scarring.
Types of Skin Damage
- Sunburn
- Premature aging (wrinkles, fine lines, age spots)
- Skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma)
- Inflammation
- Allergic reactions
- Scarring
Long-Term Consequences of Skin Damage
Skin damage caused by tanning or tattooing can have long-term consequences, including:
- Increased risk of skin cancer
- Premature aging
- Permanent scarring
- Infection
- Allergic reactions
Infection
Tanning and tattooing can both introduce bacteria and other microorganisms into the skin, leading to infection. This can occur during the procedure itself or during the healing process.
Types of Infections, Which risk is common with both tanning and tattoos
- Bacterial infections (e.g., staph, strep)
- Viral infections (e.g., herpes simplex virus)
- Fungal infections (e.g., ringworm)
Preventing and Treating Infections
To prevent infections, it is important to:
- Choose a reputable tanning salon or tattoo artist
- Follow proper hygiene practices before and after tanning or tattooing
- Keep the tanned or tattooed area clean and dry
- Use antibiotic ointments or creams if prescribed
Allergic Reactions: Which Risk Is Common With Both Tanning And Tattoos
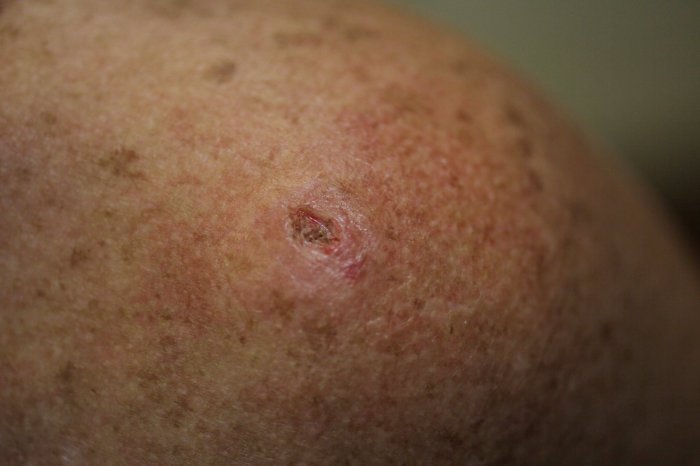
Tanning products and tattoo inks can contain allergens that can trigger allergic reactions in some people. These reactions can range from mild (e.g., itching, redness) to severe (e.g., anaphylaxis).
Potential Allergens
- Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) in self-tanning products
- Bronzers in tanning beds
- Pigments in tattoo inks (e.g., red, yellow, black)
Symptoms of Allergic Reactions
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Hives
- Anaphylaxis (difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, loss of consciousness)
Testing for Allergies
To test for allergies, a patch test can be performed. This involves applying a small amount of the tanning product or tattoo ink to a small area of skin and observing for any reaction.
Other Health Risks
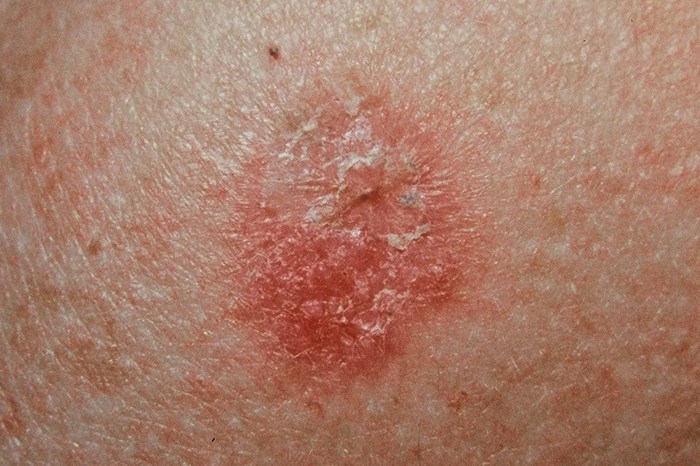
In addition to skin damage, infection, and allergic reactions, tanning and tattooing can also pose other health risks.
Eyes
- UV radiation from tanning beds can damage the eyes, leading to cataracts and macular degeneration.
Lungs
- Inhaling tattoo ink particles can irritate the lungs, causing respiratory problems.
Immune System
- Tattooing can temporarily weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Moderation and Sun Protection
When tanning, it is important to practice moderation and use sun protection to minimize the risks of skin damage. This includes limiting the number of tanning sessions, avoiding prolonged exposure, and using sunscreen with a high SPF.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
It is generally recommended to avoid tanning and tattooing during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as the potential risks to the developing fetus or infant are not fully known.
FAQ Insights
What is the most common risk associated with both tanning and tattoos?
Skin damage is the most prevalent risk shared by tanning and tattoos. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation during tanning and the presence of tattoo ink in the skin can lead to various forms of skin damage, including sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
How can I minimize the risk of infection after tanning or getting a tattoo?
Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial for preventing infections after tanning or tattooing. Avoid touching the affected area with unwashed hands, keep the area clean and dry, and follow the aftercare instructions provided by a healthcare professional or tattoo artist.
Are allergic reactions common with tanning or tattoos?
Allergic reactions to tanning products or tattoo inks can occur, although they are not as common as skin damage or infections. It is advisable to conduct a patch test before using a new tanning product or getting a tattoo to assess the risk of an allergic reaction.