In a hydronic heating system the heat transfer medium is – In a hydronic heating system, the heat transfer medium takes center stage, playing a crucial role in distributing warmth throughout a building. Understanding its properties, characteristics, and selection criteria is essential for designing and maintaining an efficient heating system.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of heat transfer mediums, exploring their types, applications, and impact on system design. We will also shed light on maintenance procedures and troubleshooting techniques to ensure optimal performance.
1. Heat Transfer Medium in Hydronic Heating Systems
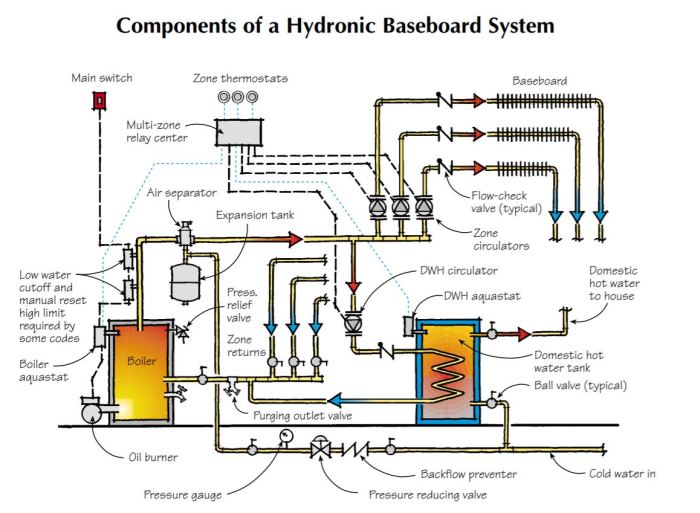
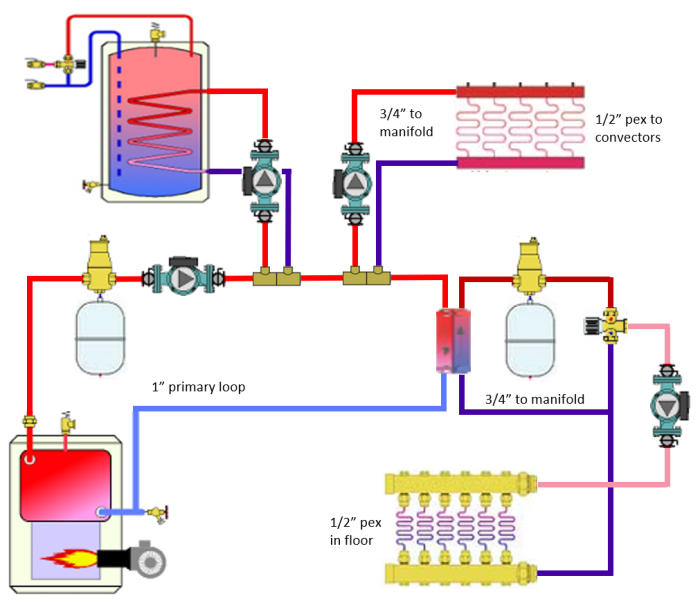
In hydronic heating systems, a heat transfer medium is used to transport thermal energy from the heat source to the heat emitters. The primary function of the heat transfer medium is to absorb heat from the heat source and release it into the heat emitters, where it is then transferred to the surrounding environment.
Common heat transfer mediums used in hydronic heating systems include water, glycol-based solutions, and thermal oils. These mediums possess specific properties and characteristics that make them suitable for use in different applications.
Factors influencing the selection of a specific heat transfer medium include:
- Specific heat capacity
- Thermal conductivity
- Viscosity
- Freezing point
- Corrosion potential
- Availability and cost
2. Types of Heat Transfer Mediums
| Medium Name | Composition | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O |
|
|
| Glycol-based solutions | Ethylene glycol or propylene glycol mixed with water |
|
|
| Thermal oils | Synthetic hydrocarbons |
|
|
Water is the most commonly used heat transfer medium due to its low cost and high specific heat capacity. Glycol-based solutions are used in applications where freezing is a concern, such as outdoor installations. Thermal oils are used in high-temperature applications, such as industrial processes.
3. Hydronic Heating System Components
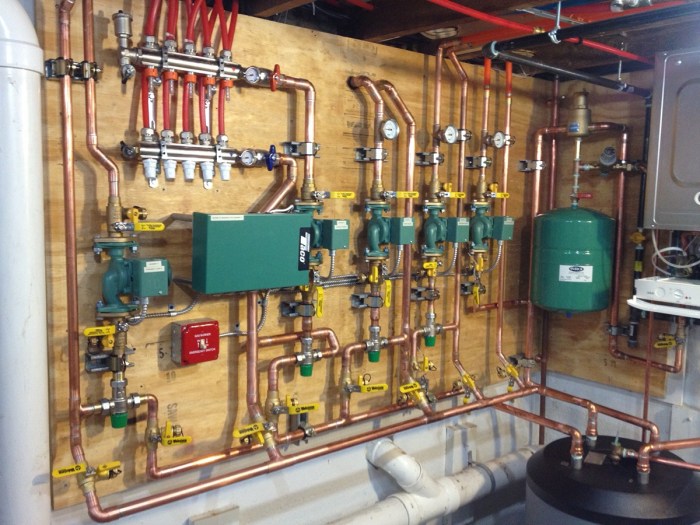

A typical hydronic heating system consists of the following components:
- Heat source: The heat source can be a boiler, furnace, or heat pump.
- Distribution pipes: The distribution pipes carry the heat transfer medium from the heat source to the heat emitters.
- Heat emitters: The heat emitters release heat into the surrounding environment. Common types of heat emitters include radiators, baseboards, and radiant floor panels.
The heat transfer medium circulates through the system, absorbing heat from the heat source and releasing it into the heat emitters. The circulation of the heat transfer medium is typically achieved using a pump.
4. System Design Considerations
When designing a hydronic heating system, several key factors need to be considered:
- Heat load: The heat load is the amount of heat required to maintain the desired temperature in the space being heated.
- Heat transfer medium: The choice of heat transfer medium impacts the system design parameters, such as pipe size, pump size, and heat emitter selection.
- System configuration: There are different system configurations available, such as one-pipe systems, two-pipe systems, and radiant floor systems. The choice of system configuration depends on the specific application.
5. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance of a hydronic heating system. Common maintenance procedures include:
- Checking the heat transfer medium level and adding makeup fluid as needed
- Bleeding air from the system
- Cleaning or replacing filters
- Inspecting and cleaning heat emitters
Potential issues related to the heat transfer medium include:
- Leaks
- Corrosion
- Freezing
Troubleshooting techniques include:
- Identifying the source of the leak and repairing it
- Flushing the system to remove corrosion products
- Adding antifreeze to the heat transfer medium to prevent freezing
Questions and Answers: In A Hydronic Heating System The Heat Transfer Medium Is
What is the most common heat transfer medium used in hydronic heating systems?
Water is the most commonly used heat transfer medium due to its high heat capacity, low cost, and non-toxic nature.
What factors should be considered when selecting a heat transfer medium?
Factors to consider include heat capacity, viscosity, thermal conductivity, chemical stability, and compatibility with system components.
How does the heat transfer medium interact with the components of a hydronic heating system?
The heat transfer medium circulates through pipes, absorbing heat from the heat source and releasing it to heat emitters, such as radiators or radiant floor panels.